The first international standard for certifying greenhouse gas (GHG) neutral organizations and products, ISO 14068-1, was published in November 2023. As part of the ISO 14060 family, this standard builds on existing guidelines for GHG quantification, reporting, validation, and verification. ISO 14068-1 provides a comprehensive framework for achieving carbon neutrality, offering clear definitions, principles, and requirements for both organizations and products.
Fundamentals
ISO 14068-1 addresses the increasing number of companies claiming GHG neutrality for their businesses or products, highlighting the need for a consistent framework that minimizes ambiguity. By establishing clear criteria and certification processes, the standard aims to combat greenwashing and reduce conflicting claims. It also supports companies, customers, and regulatory bodies in assessing the integrity and credibility of carbon neutrality statements.
How is the ISO 14068-1 structured
The ISO standard defines Carbon neutrality as a period during which the carbon footprint has been reduced through GHG emission reductions or removals and, if greater than zero, is then counterbalanced by offsetting. This definition is consistent with the IPCC definition of GHG neutrality, where neutrality is achieved when a company’s gross GHG emissions are balanced by an equivalent amount of CO2 removed from the atmosphere.
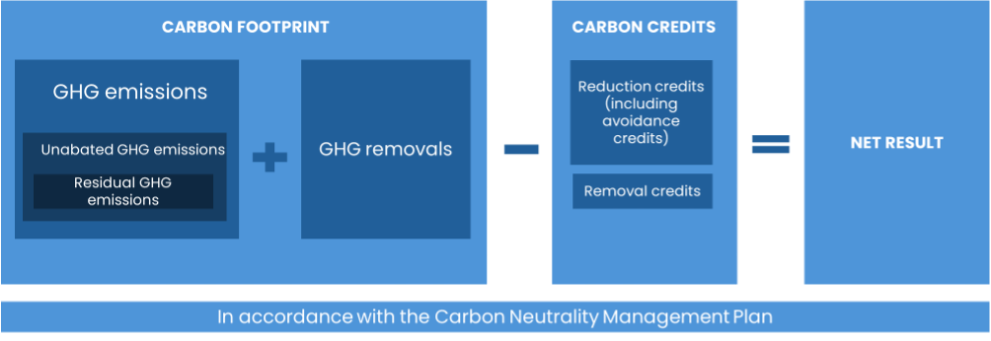
The approach follows a hierarchical structure that prioritizes GHG emission reductions over carbon offsetting. To claim carbon neutrality, an entity must reduce its carbon footprint and then offset any remaining emissions with carbon credits (see Figure 1).
Further, the standard defines the systematic process, consisting of several steps, the entity must follow to claim carbon neutrality:
- 6: Commitment to Carbon neutrality
- 7: Selection of the subject and its boundaries
- 8: Quantification of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and GHG removals
- 9: Carbon neutrality management plan
- 10: Quantification of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and GHG removals
- 11: Offsetting the carbon footprint
- 12: Carbon neutrality report
- 13: Carbon neutrality claims
Steps 8 to 13 must be repeated for each reporting period.
Furthermore, the standard defines criteria for carbon credits and carbon credit programs, including the acquisition and retirement of ex-post certificates and the prevention of double counting. To enhance transparency, a publicly accessible report must include details about the subject matter, management plan, carbon footprint and its components, calculation methods used, and information on the projects and certificates utilized for offsetting. An entity can only claim carbon neutrality if all standard requirements are met, a detailed summary is published, and the accuracy and integrity of the information are verified.
How DFGE can support
DFGE offers comprehensive support in line with scientific standards on climate strategy. The process begins with calculating the carbon footprint using DFGE’s proven top-down approach, setting goals and identifying CO2 reduction potentials, avoiding CO2 emissions, and then moving on to CO2 reporting and offsetting for a CO2-neutral company or product. To achieve CO2 neutrality, the DFGE follows the ISO 14068-1 standard. If you have any further questions about our service, please contact us by e-mail or by phone +49 8192 99733-20.
Sources
https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg3/downloads/report/IPCC_AR6_WGIII_FAQs_Compiled.pdf









